article Content
Today, in the end Google Pixel is a failed competitor to the Apple iPhone, Android 7.1, which didn’t bring almost anything new, the death of Cyanogen OS and CyanogenMod uncertain future, new tools for interface design in the style of the Material, comparing the Google Assistant and Siri, a story about a secure Protocol Signal and WhatsApp and proof of the absolute futility of most Android apps to encrypt data. Happy reading!
Events
the Main event of the October is, of course, to market Google Pixel. New Google smartphone was presented to the fourth number as a new stage of development of mobile lines Google. This is not the nexus, which was just licensed from third parties, and smartphone completely designed by Google and not focused on developers, and a wide range of users; the kind of protracted response to Apple with its iPhone, its price and approach “symbiosis of hardware and software that complement each other.”
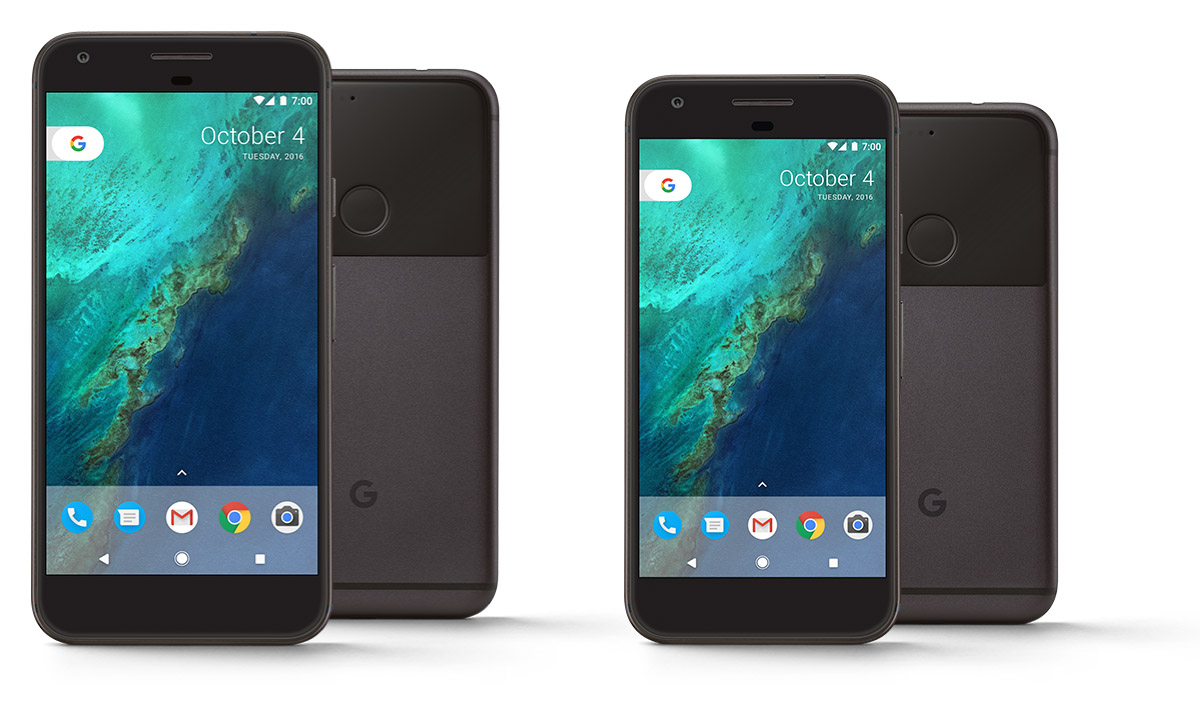

the Answer, I must say, was very contradictory: overall, a really decent machine with excellent performance, ergonomics, with buns in the form of faster updates and round-the-clock telephone support, but too ambiguous by design and especially price. Many obzorschiki agreed that Pixel is simply not worth the money he asked for, and besides the great camera and the official support, Pixel no longer stands out from other high-end smartphones.
Pixel — only at the moment, the smartphone, running Android 7.1. This version was presented on October 11 in the Preview builds for Nexus 5X, 6P Nexus and Pixel C. the new version has the shortcuts to app icons in the style of iOS 9 (long hold finger on the icon will open the quick actions menu), support for round icons and other small improvements in the user interface.
he Distinguished himself in October, and Samsung, but rather continued to Excel in history with an exploding Note 7. It turned out that the new marked as Safe (safe) smartphones with replaced battery exploded not worse than the previous. The US and many international airlines fully banned include the smartphone aboard the aircraft, and the cost of Samsung fell by 8%, which means a loss of about $ 17 billion.
never having dealt with the cause of the fire, Samsung has initiated a recall of all Galaxy Note 7, as to somehow retain customers, offered not only a refund, but a discount of $ 100 on the purchase of another model. Interestingly, almost immediately after the opinion Note 7, the Chinese company Xiaomi announced the Mi Note phablet 2 c are absolutely identical curved screen 5.7″ like Note 7. And of course, this immediately gave rise to rumors about draining the already manufactured lot of useless screens to Note 7 to the Chinese.
Sad news for users of custom firmware: Cyanogen, the company stops the development of Cyanogen OS is a commercial version of CyanogenMod and switches to develop so-called modular OS, which essentially means the transformation of the company from a developer of a full operating system to developer of software for Android. For CyanogenMod this is unlikely to be the end, but it is likely that the development of the firmware will slow down, and the new functionality will appear less often.
Releases
In Chrome Canary appeared version that includes all the latest, but still unstable innovations browser. This so-called bleeding edge for the most daring and desperate, those who beta seem to be too stable and boring.
- Material Design — a new set of tools for application developers Material Design: Gallery is a platform for sharing design concepts with the history of versions (a kind of GitHub for designers), Stage and Remixer — prototyping tools to make the layout of the interface and to test how its elements work (including animations).
- Global Android Device Directory — a comprehensive directory of Android smartphones, sorted based on popularity in individual countries and around the world. In addition to the standard “Model” and “Android Version”, the catalog includes data such as average response latency (ping) to mobile and Wi-Fi networks and even the percentage of application failures.
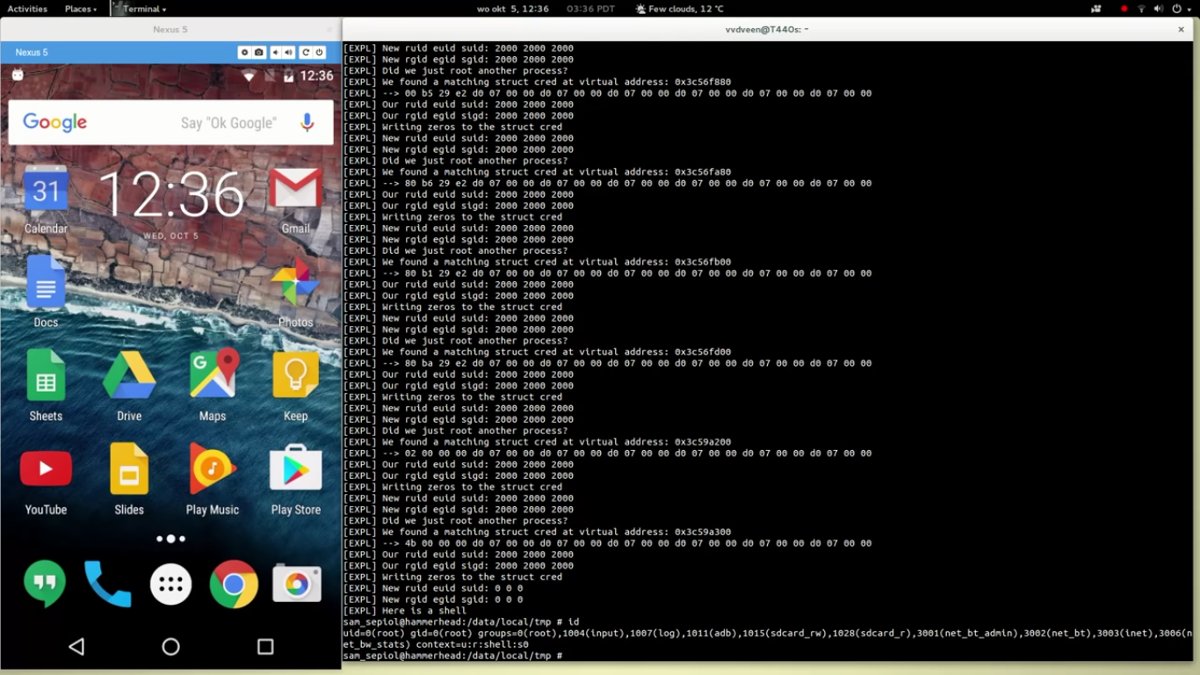
- Drammer is a universal exploit that allows you to get root access on many Android smartphones using a vulnerability Rowhammer. The last threat that is only “iron” the problem of memory and can not be fixed with updates. For a video demonstration.
View
Read
Root for Pixel (XL) / SuperSU v2.78 SR2 developer Chainfire, known thanks to the management of root-SuperSU powers, and apps FlashFire, and Recently CF.lumen, tells how he implemented support for SuperSU Google Pixel.
To allow apps to obtain root access in the system must be at least two components: the su binary file in Linux used to execute commands with root privileges, and processing application requests root access and display a notification on the screen.
Early apps for rooted placed these components in the system: su binary in /system/bin (or /system/xbin), and app (Superuser.apk or SuperSU.apk) in /system/app. But in this approach problem is: the firmware update or erase them, or simply not installed (if it is not about incremental upgrades). Then Chainfire has decided to place these components in the RAM-disk that is loaded into memory right after the kernel. This approach does not prevent updates, and worked fine before the release of 7.0 and Android smartphones Pixel.
it Turned out that the RAM disk they use only when booting into recovery, while the contents of “system” RAM disk is in the system. Moreover, as the partition system is mounted as root and not the directory /system. To solve this problem, I had to create a utility that generates a RAM-disk again, modifies the kernel so that it loaded the RAM disk. Moreover, that it correctly worked, a utility itself must be loaded from the RAM disk.
How to compile DVIA 10 for iOS 8 and Xcode for mobile app security testing — how to compile and install Damn Vulnerable iOS App (DVIA) for iOS 10. DVIA, or “Damn vulnerable app”, developed a Career, Gianchandani (Prateek Gianchandani) specifically as a test site for specialists and anyone interested in security and hack mobile applications.
Password Storage In Apps Sensitive — a story about what protection actually invites applications for information security on the SD card. For example, it turned out that the app Private Photo Vault with a rating of four stars and the number of downloads from one to five million protects files with a four-digit PIN code, which is stored in the application directory in the form of a SHA-1 hash. Having root access, you can retrieve the SHA-1 hash of the application and using a simple script to pick it up for a couple of seconds.
How the Textsecure Protocol (Signal, WhatsApp, Facebook, Allo) Works — principles of operation of the Textsecure Protocol, which first appeared in the messenger Signal and is used today in many popular messengers. The paper briefly but succinctly describes the Protocol used in cryptographic algorithms, the method of key exchange, the connection is established, the limitations of the Protocol and its vulnerability.
Six Reasons You Should Stop Using WhatsApp — six reasons to stop using WhatsApp. Spoiler: the essence of the article is that, despite the end-to-end encryption for all chat, WhatsApp saves the conversation history in the cloud, iCloud or Google Drive unencrypted, and shares the metadata of your messages (with whom and when you communicated) with Facebook.
KNOXout — Bypassing Samsung KNOX — a study of the system RKP (Real-time Kernel Protection) designed to protect Android smartphones from the exploits of the kernel. The author describes how this system works and how to get around.
Pork Explosion Unleashed — a story about a backdoor code found in the loader some produced by Chinese company Foxconn (the same one that assembles the iPhones) smartphones. In particular, a backdoor was discovered in smartphone InFocus M810, and Nextbit Robin and allows you to get root access without even having to unlock your smartphone with a PIN. Everything you need — connect by using USB cable.
No comments:
Post a Comment